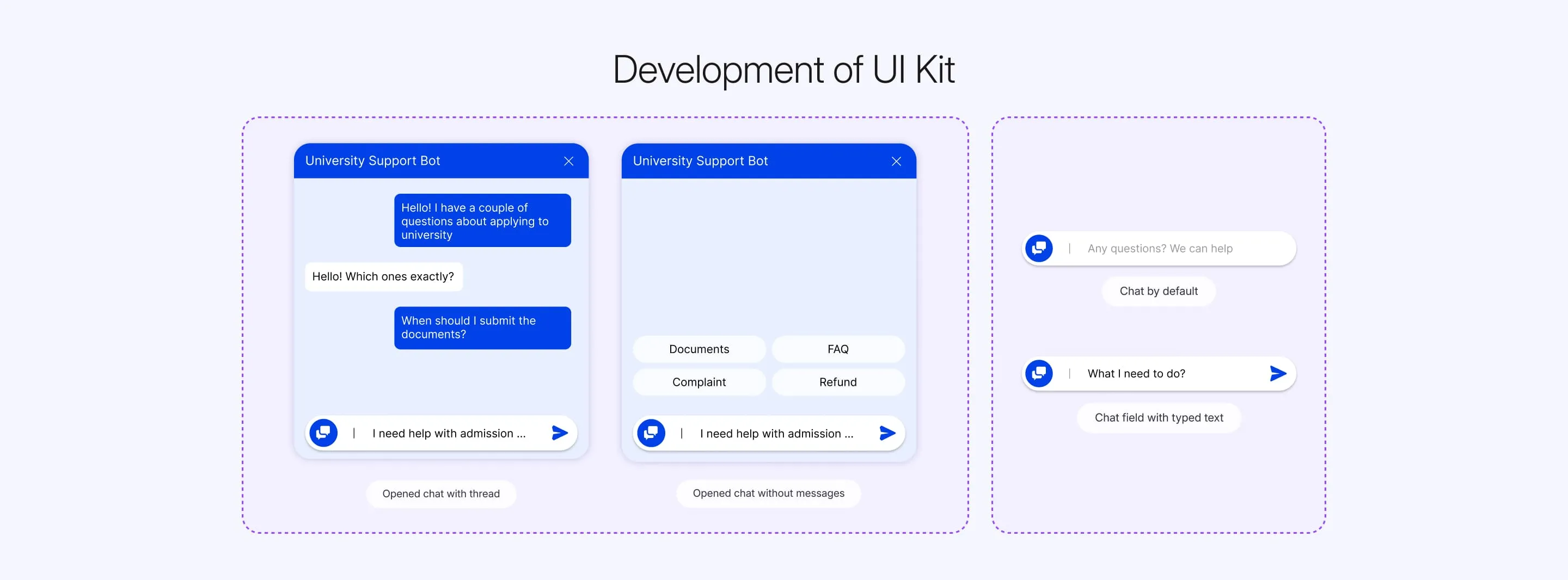
Smart Assistant
To help the university solve all its tasks, we decided to develop a smart chatbot based on LLM (large language model). The university collaborates with Microsoft Corporation, thus having full access to the infrastructure for creating such a tool.
We became partners with the educational institution and took on the development of the chatbot based on a set of Microsoft products: Azure and Dynamics base.